The mpox virus, formerly known as monkeypox, is an important health concern that has recently gained attention in Nigeria.
This rare viral disease is endemic to Central and West Africa and can spread through both animal-to-human and human-to-human contact.
Transmission and Spread
Mpox primarily spreads from animals to humans.
This occurs through direct contact with the blood, body fluids, skin, or mucosal lesions of infected animals such as monkeys, squirrels, and rodents.
Handling or consuming inadequately cooked bushmeat from these animals poses a significant risk.
Human-to-human transmission happens when a person comes into contact with an infected individual’s bodily fluids or contaminated materials, including clothing and bedding.
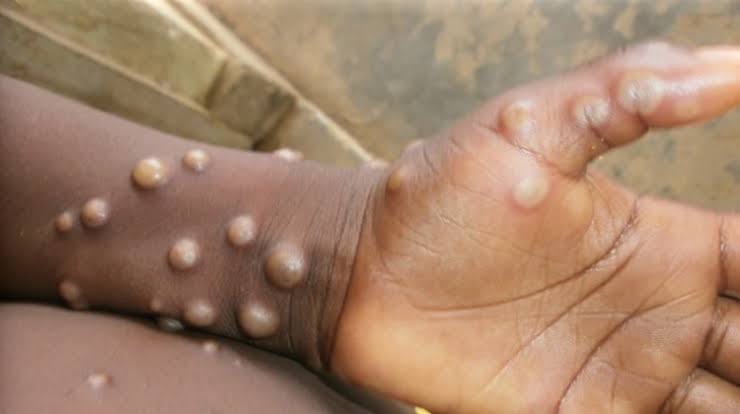
Symptoms of Mpox
The disease typically starts with fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue.
A distinctive rash usually develops, beginning on the face and then spreading to other parts of the body.
The illness can range from mild to severe, and complications may arise, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
People Also Read: 5 Things You Can’t Do Permanently After Getting BBL
Mpox Prevention
Preventing mpox involves several key practices:
1. Avoid contact with wild animals
Refrain from handling or consuming bushmeat and ensure it is thoroughly cooked.
2. Maintain good hygiene
Regular hand washing and disinfecting surfaces can reduce the risk of infection.
3. Practice safe contact
Avoid close contact with individuals displaying symptoms of mpox and use protective clothing if necessary.
By understanding these aspects of mpox and following preventive measures, Nigerians can better protect themselves and their communities from this emerging health threat.
