The Federal Capital Territory Administration (FCTA) announced on Monday, July, 3, 2023, that diphtheria, a serious and very contagious disease, has broken out in Abuja.
The announcement was made at a press conference addressed by the director of public health, Dr. Sadiq Abdulraman.
He called on residents of the FCT to immediately take the vaccine (the pentavalent vaccine) to break the spread of the disease, which he explained is an infection of the nose and throat that’s easily preventable by the vaccine.
In order to take preventive measures, here are some things to know about the disease.
Transmission
Diphtheria spreads through respiratory droplets from an infected person, usually through coughing or sneezing. It can also be transmitted by touching objects contaminated with the bacteria.
Symptoms
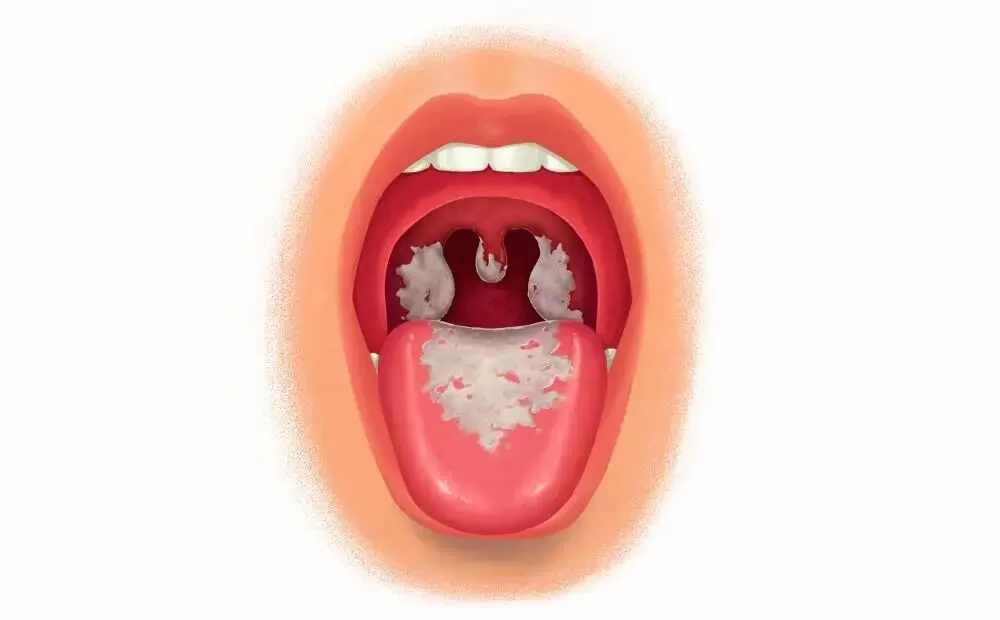
The symptoms of the disease can vary, ranging from mild to severe. Common signs include a sore throat, fever, swollen glands in the neck, and difficulty breathing.
A grayish-white membrane may form in the throat, which can obstruct the airway and cause serious complications.
Vaccination
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent diphtheria. The diphtheria vaccine is typically administered as a combination vaccine called DTaP or Tdap, which also protects against tetanus and pertussis (whooping cough).
It is recommended for children and adults to maintain immunity.
Prevention
Besides vaccination, good hygiene practices can help prevent the spread of diphtheria. This includes regular handwashing, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
Treatment
Diphtheria requires immediate medical attention. The primary treatment involves administering diphtheria antitoxin, which neutralizes the toxin produced by the bacteria.
Antibiotics are also given to clear the infection. Patients are often isolated to prevent the spread of the disease.
Complications
If left untreated, diphtheria can lead to severe complications, including myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), nerve damage, kidney problems, and respiratory failure.
These complications can be life-threatening.
Global Impact
While diphtheria has become rare in many developed countries due to widespread vaccination, it still poses a significant health risk in areas with limited access to vaccines and healthcare.
Outbreaks can occur, particularly in under-immunized or unvaccinated populations.
Here’s another great read for you: 3 Foods To Avoid If You Have Diabetes

