
All over the world February 6th has been marked as the International day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation usually referred to as female circumcision. In Nigeria Female Genital Mutilation is still practiced in spite of the numerous health issues and complications of FGM. In this chat with iBrandTV, Dr Esther Oluwatosin, a Gender and Reproductive Health Analyst sheds more light on FGM, how complications can be managed, benefits of not being circumcised as a woman and other sundry issues.
In simplified terms what is FGM?
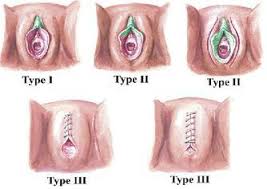
FGM is female genital mutilation or female circumcision, is the partial or total removal of female external genitalia due to non medical reasons. There are four types
Type 1: Partial or total removal of clitoris or prepauce.
Type 2 : Type 1 and removal of labia Minora (external lip) with or without the majora
Type 3 : Narrowing of the external genitalia
Type 4: It includes all other forms including pickling, piercing and incising.
Nigeria is one of the countries that are still practicing it, what do you have to say about this? The implication and the burden as a whole?
Nigeria is one of the seven countries which accounts for over 200 million girls and women who are mutilated.
Though the incidence is dropping but the practice still persists because of gender inequality, the belief that it can curb promiscuity, it must be part of the rite of passage, weak enforcements of laws and recently medicalization, currently five states accounts for the high burden of cases : Ekiti, Osun, Imo, Ebonyi and Oyo.
What is the prevalence rate in these state?
In Oyo=55.0%, Osun=67.8%, Ebonyi=43.2%,Imo=51.6% and Ekiti=62.6%
What is the source of this data and does that mean we are winning the war against FGM in Nigeria?
Multiple indicator cluster survey 2016-2017 conducted in all states
Why is this so?
Osun accounts for a high number of cases due to deep seated cultural norms including prevention of promiscuity, family ritual which must be done for all women to clean and free of evil spirits, weak enforcement of laws and medicalisation of FGM.
Knowing that it is a cultural issue, UNFPA has since 2014 engaged community, traditional and religious leaders to have a consensus to abandon FGM. Currently, we have over 600 anti FGM champions conducting door to door counselling on the need to abandon FGM in the five states.
Widely believed that females that go through Genital Mutilation do not enjoy Sex or Love making, how true is this submission?
Due to the complications of FGM, women find it difficult to enjoy sex because the external female organ, the clitoris which ensure lubrication during sex has been cut off. In some cases, the external organ have been sown up.
Apart from not enjoying sex, what other implications can this have on women?
Infertility, pelvic inflammatory infections, menstrual pains, keloids, obstructed labour are some of the implications of FGM. FGM can cause obstructed labour due to the narrowing of the external genitalia.
Is there a medication for females that are circumcised to aid lubrication in other to enjoy sex?
Lubricants can be used but it will not total resolve the pain. Depending on the type of FGM, corrective surgery can be done to open the external genitalia to allow for easy passage of the male external genitalia.
Is there surgery for all types of FGM. Also is there an age limit for such surgery?
Yes and there is no age limit.
Does FGM have any effect in Child delivery?
Women with type 2 and 3 are most at risk during delivery.
As a medical doctor, what are the benefits of not being circumcised as a woman?
There are huge benefits both for short term and long term: There is no risk of gynaecological problems including, paining mensuration, repeated pelvic infections,infertility, urinary tract infections sexual intercourse will not painful, there is no risk of obstructed labour
Apart from the huge success you recorded in Osun what has been the impact in other states?
In other states collectively, over 1,500 communities have declared abandonment of FGM, all states have VAPP laws in place to prosecute perpetrators, each state has a state technical committees that ensures compliance, 300 heath care workers have also been trained to offer services to women with complication.
We also have champions in other state advocating against FGM. We equally engage youth social media advocates to create awareness among girls.
Last year UNFPA supported Federal government to revise their National Policy and plan of action on FGM
All five states now have adopted the Violence against person prohibition act which put in place sanctions on perpetrators. All supported by UNFPA
How will you rate Nigerian government in the campaign against FGM?
The government is putting in a lot to ensure its eradicated. But the government still need to do more by creating more awareness and enlightenment programmes to dispel myths.
Ensure all laws are enforced who ever is the perpetrators. Provide essential services to survivors to alleviate the complications. Involve young girls as advocates to fight against FGM practice
Engage with the traditional leaders and religious leaders to ensure the abandonment of FGM

