With the novel coronavirus pandemic code-named COVID-19 currently raving across the world, iBrandTV have put together a glossary of key terms for everyone to be well informed.
As at today, more than three million cases of coronavirus have been officially registered across the world, with nearly 80 per cent in Europe and the U. S.
According to a tally by AFP at 2050 GMT Monday using official figures.
At least 3,003,344 infections have been detected, including 209,388 deaths, mostly in Europe where there are 1,393,779 cases and 126,233 deaths.
Here are the terms.
Asymptomatic
When carriers of a disease do not show signs or symptoms of a disease, but can still transmit it. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), COVID-19 likely has a two to 14-day incubation period, based on what they have seen with other coronaviruses.
READ ALSO: Nigeria records 64 new cases of COVID-19, total infections now 1337
Case fatality rate (CFR)
The death rate. An estimate of the risk of mortality from a contagious disease. The CFR is calculated by dividing the number of deaths caused by a disease by the number of cases of that disease in a given time period.
Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine
Drugs primarily used to treat and prevent malaria. Clinical trials of these drugs are underway, but early evidence is still not clear they prove useful.
Close contact
A person who may be at risk of a contagious disease because of their proximity or exposure to a known case. For COVID-19, the CDC defines a close contact as anyone who has been within 6 feet of a person infected with the virus for a prolonged period of time, or has had direct contact with the infected person’s secretions.
Cluster
A disease cluster or infection cluster is a group of similar health events that have occurred in the same area around the same time.
Community transmission/spread
Infections identified in a given geographic area without a history of travel elsewhere, and no connection to a known case.
Confirmed cases
The number of cases that have been confirmed by diagnostic testing. The actual number of cases that exist is likely much higher.
Contact tracing
The process of identifying, assessing and managing people who have been exposed to a contagious disease to prevent onward transmission.
Cordon sanitaire (see also isolation, quarantine)
The restriction of movement in and out of a region or city, which prevents anyone from leaving a defined geographic area infected by a disease to stop its spread.
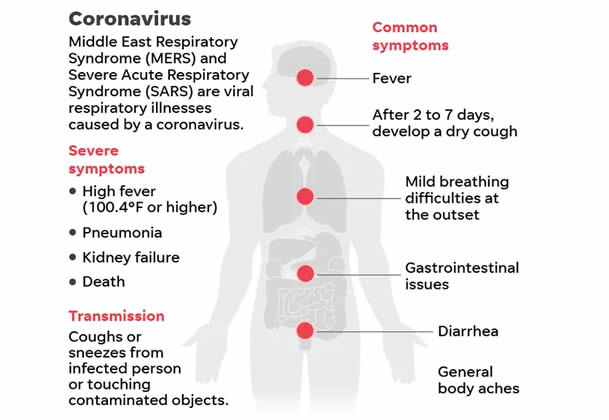
Coronavirus
A family of viruses that cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases, such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS-CoV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV). The novel coronavirus recently discovered has been named SARS-CoV-2, and it causes COVID-19.
COVID-19
The name of the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, which is short for “Coronavirus Disease 2019.” If you’re sick, you have COVID-19. You were infected by SARS-CoV-2.
Drive-through testing
Testing in which individuals remain in their vehicles, and medical staff in protective gear come to administer the swab test. Afterward, swabs are sent to a laboratory for testing.
Droplet transmission/spread
A mode of transmission for a contagious disease that involves relatively large, short-range — less than 6 feet — respiratory droplets produced by sneezing, coughing or talking.
Elective surgeries
Procedures that are considered non-urgent and non-essential. During periods of community transmission, the CDC is recommending that elective procedures, surgeries and non-urgent outpatient visits be postponed.
Endemic
A disease that regularly infects humans, like the flu, strep throat or any common illness. There are four coronavirus strains that commonly infect humans, usually manifesting as colds.
Epidemic
An increase, often sudden, in the number of cases of a disease above what is normally expected in that population in that area. When there are enough outbreaks, in places beyond that initial spot, that amounts to an epidemic.
Essential Activities
Tasks that are essential to an individual’s health or safety or the health and safety of their family or household members, which may include obtaining food or medicine, seeking urgent medical attention or other necessary purposes.

