In today’s rapidly evolving media landscape, young journalists need to equip themselves with a diverse set of digital skills to thrive.
As traditional journalism converges with digital media, mastering these digital skills becomes essential.

This is not only for effective storytelling but also for staying competitive in the industry. Here are some key digital skills that young journalists should acquire:
1. Digital Research And Verification
Advanced Research Skills
As artificial intelligence comes into content creation, the dissemination of misinformation and disinformation has been on the rise.
For this reason, it is important that a young journalists should know how to efficiently gather information from credible online sources.
This includes using advanced search techniques, accessing digital databases, and utilizing open-source intelligence (OSINT) tools to find accurate information.
Fact-Checking And Verification
In an era of misinformation, knowing how to verify facts, images, and videos is crucial. Journalists should familiarise themselves with tools like Google Reverse Image Search, InVID, and FactCheck.org to ensure the authenticity of their sources and content.
2. Multimedia Storytelling
Video And Audio Production
Back in 2019, I had researched the trend and future of journalism, and I saw that multimedia would be a major driver of this era we are now in.
At that time, I begin to acquire skills around video and audio editing.
Now, skills in video editing, audio recording, and podcasting are valuable for creating dynamic multimedia content.
Journalists should learn to use software like Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, or even free tools like Audacity for audio production.
Photography And Photo Editing
Visuals are a core part of digital storytelling. Young journalists should understand the basics of photography, as well as how to edit and enhance photos using tools like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom.
3. Data Journalism and Visualization
Data Analysis And Interpretation
Analyzing datasets to uncover trends, patterns, or insights can add depth to reporting.
Familiarity with tools like Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or even more advanced platforms like Tableau and Python can be highly beneficial.
Data Visualisation
Creating visual representations of data helps readers understand complex information quickly.
During the last Nigerian election, I created a map that would give you a vivid reflection of what party won which state as the results were being collated.
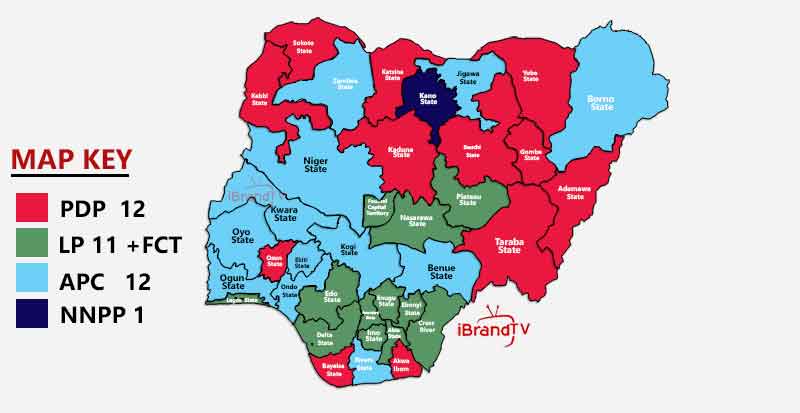
Journalists should explore tools like Datawrapper, Infogram, or Google Data Studio to produce compelling charts and graphs while reporting their contents.
4. Social Media Management and Content Creation
Social Media Proficiency
Journalists need to be adept at using platforms like Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn for news dissemination and audience engagement. Understanding how to craft content that resonates with different audiences on these platforms is key.
Analytics And Audience Insights
Knowledge of social media analytics tools, such as Hootsuite, Buffer, and native platform insights, helps journalists track audience engagement, understand content performance, and refine their strategies.
5. SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) And Content Optimisation
SEO Basics
Also, understanding SEO can help journalists ensure that their content reaches a wider audience.
Learning the fundamentals of keyword research, on-page optimisation, and the use of SEO tools like Google Keyword Planner or Yoast SEO can improve the visibility of their stories.
Writing For The Web
Journalists should know how to write in a way that is both engaging and optimised for search engines.
This includes crafting compelling headlines, using subheadings, and formatting content for easy online reading.
6. Mobile Journalism (MoJo)
Mobile Reporting Tools
With the rise of mobile journalism, journalists need to know how to report, shoot, and edit stories directly from their smartphones.
Apps like Filmic Pro, Capcut, LumaFusion, and Adobe Premiere Rush are popular for mobile reporting and editing.
Live Streaming
Young journalists should learn how to live stream events or breaking news on platforms like Facebook Live, YouTube, or Periscope, enabling real-time reporting and audience interaction.
7. Basic Coding And Web Development
HTML, CSS, And JavaScript
A basic understanding of coding can help journalists customise their content on websites or troubleshoot minor issues.
While in Vice of Nigeria, I had an opportunity of learning how to code. That offered me a knowledge of HTML and CSS.
Indeed, familiarity with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript basics can be a valuable asset for digital journalists.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
Journalists should know how to use popular CMS platforms like WordPress, Drupal, or Joomla to publish and manage content.
This knowledge can also help them collaborate more effectively with web developers and designers.
8. Cybersecurity And Digital Ethics
Cybersecurity Awareness
Journalists must be vigilant about protecting their digital identities and sensitive information.
They should be familiar with secure communication tools like Signal, and use practices like two-factor authentication, encrypted emails, and strong password management.
Digital Ethics And Privacy
Young journalists should understand the ethical considerations around online privacy, copyright laws, and responsible reporting in the digital age.
This includes knowledge of fair use, digital rights, and respecting the privacy of individuals in online content.
9. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation Tools
AI In Journalism
With the growing use of AI in content creation, journalists should understand how tools like ChatGPT or Jasper can aid in research, drafting, or editing.
They should also stay informed about AI’s ethical implications in journalism.
This will help them understand possible manipulations that could happen to contents – images, videos and graphics to identify where there is misinformation or disinformation.
Automation For Workflow Efficiency
Automation tools like Zapier, IFTTT, or even Google Scripts can help journalists streamline repetitive tasks, such as distributing content across multiple platforms or organizing their research.
10. Collaborative Tools And Project Management
Project Management Software
Journalists often work in teams and need to manage their projects effectively.
Familiarity with tools like Trello, Asana, or Slack can enhance collaboration and productivity.
Cloud Storage And Document Sharing
Knowing how to use Google Workspace or Microsoft OneDrive for collaborative work and document sharing is essential, especially in remote work settings.
You see, by mastering these digital skills, young journalists can enhance their storytelling abilities, engage with wider audiences, and adapt to the dynamic demands of modern journalism.
As the media industry continues to evolve, these skills will not only bolster their careers but also contribute to more informed and digitally-savvy journalism.

